How Muscles Work
This article is targeted at a young audience. It is not meant to be scientific. It is a simplistic overview, and terminology and language is aimed at a young audience.
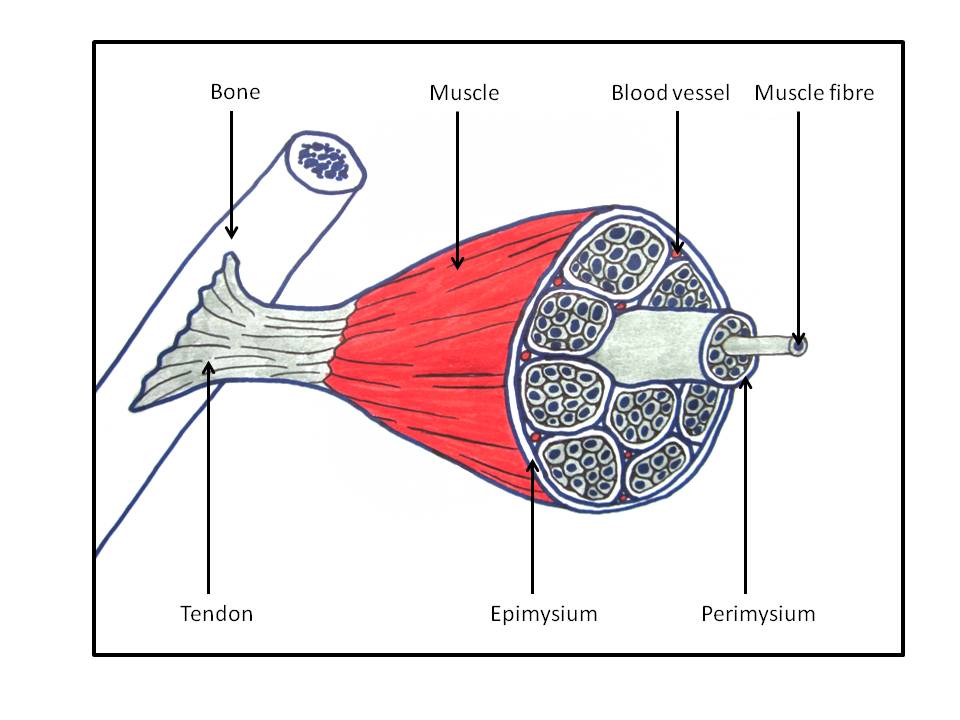
A muscle contains a whole lot of little fibres, kind of like how a rope is made up of a lot of little strands.
When you use (contract) your muscles, these little fibres all get shorter.
You can only make a muscle shorter (contract). Once you have made it short, you need to use a muscle on the other side to pull it back out. Muscles work together.
Strength is the maximum mass a muscle can pull.
Endurance is how long a muscle can pull less than its maximum mass.
Power is how fast the muscle can pull its maximum mass.
Flexibility is how long a muscle can become without breaking.
Increasing Flexibility...
As we get stronger, the muscle fibres get fatter and shorter. Because the muscle fibres get shorter, the muscle can’t stretch as far.
To make the muscle be able to stretch out longer, we need to make the muscle fibres longer. The way we do this is by "breaking" the fibre. Your body then repairs the fibre, but makes it longer at the same time.
So, to get more flexible you need to do a little bit of damage to your muscles. This means that stretching will need to be uncomfortable.
Some Muscle Names
Front (Anterior)
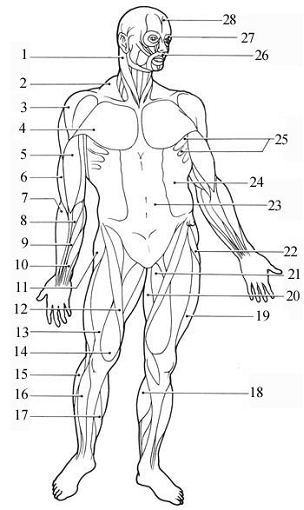
- Sternocleidomastoid - rotate or bow the head. (prayer muscles)
- Trapezius
- Deltoid - the prime mover of arm abduction.
- Pectoralis - adduct and flex the arm.
- Biceps brachii - the prime mover for forearm flexion and supination.
- Brachialis
- Brachioradialis
- Flexor carpi radialis - flex the wrist and abduct the hand.
- Palmmaris longus
- Flexor digitorum superficialis - flex the wrist and abduct the hand.
- Gluteus medius
- Sartorius - the synergist to bring about the cross-legged position.
- Rectus femoris - produces the kicking motion of the knee.
- Vastus medialis - flex and invert the foot.
- Peroneus longus
- Tibialis anterior - flex and invert the foot.
- Soleus
- Gastrocnemius - the prime mover for pointing the toes. (toe-dancer's muscle)
- Vastus lateralis
- Gracilis
- Adductor longus
- Tensor fasciae latae
- Rectus abdominis
- External abdominal oblique
- Serratus anterior
- Orbicularis oris - close the mouth and protrude the lips. (kissing muscle)
- Orbicularis oculi - close the eyes, squint, and blink.
- Occipitofrontalis - raise the eyebrows and wrinkle the forehead.
Back (Posterior)
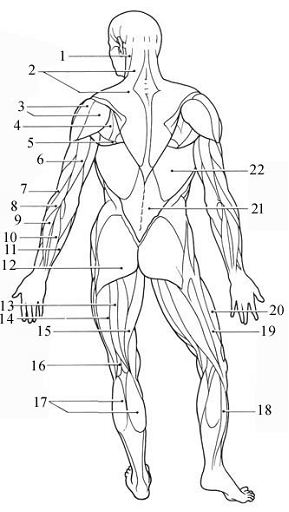
- Sterncleidomastoid - rotate or bow the head. (prayer muscles)
- Trapezius
- Deltoid - the prime mover of arm abduction.
- Infraspintus
- Teres major
- Triceps brachii
- Brachioradialis
- Extensor carpi radialis
- Extensor digitorum
- Extensor digiti minimi
- Extensor carpi ulnaris
- Gluteus maximus
- Biceps femoris
- Semitendinosus
- Gracilis
- Semimembranosus
- Gastrocnemius
- Soleus
- Fascia lata
- Vastus lateralis
- Thoracolumbar fascia
- Latissimus dorsi

